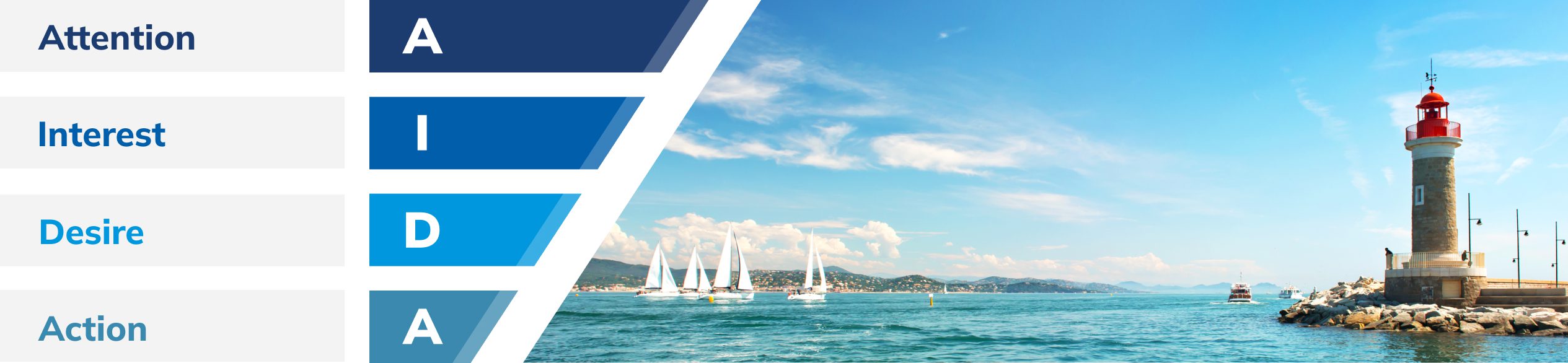
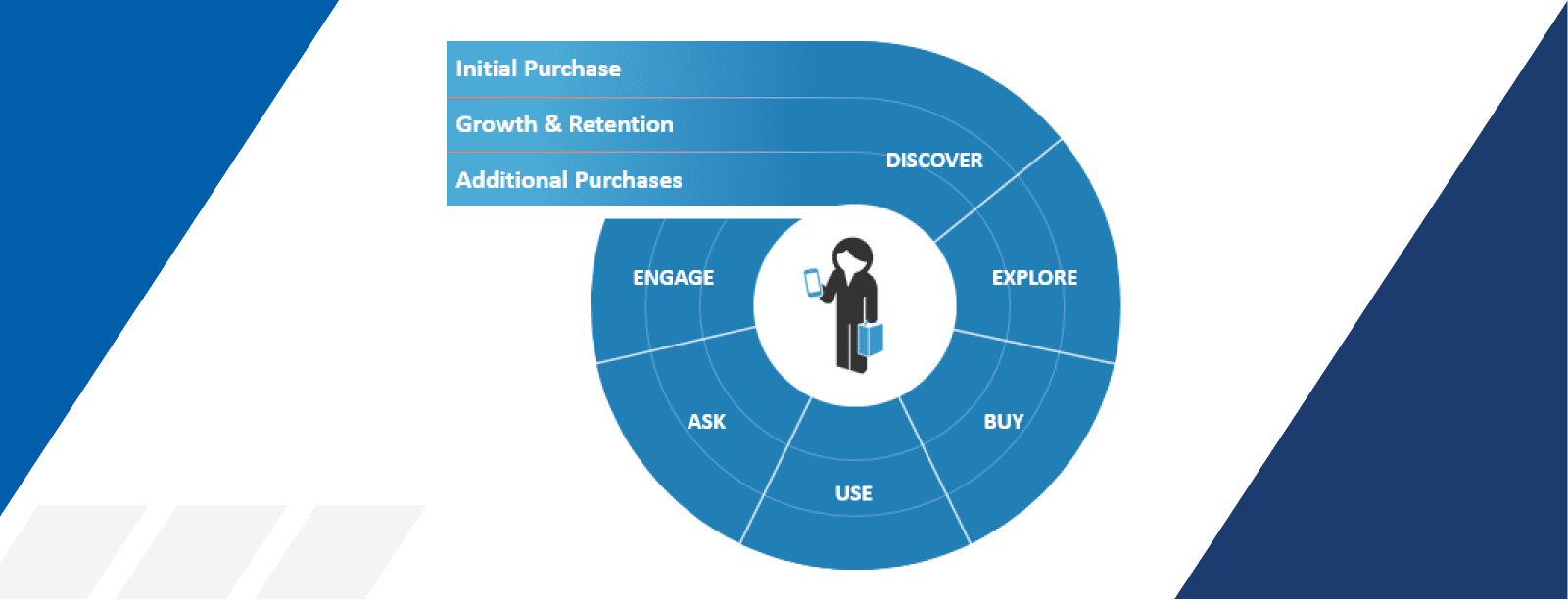
1. Initial consideration set: In the classic sales funnel, this is referred to as the 'awareness' stage. Content that addresses common queries and establishes authority, such as guides and tools, should be a priority at this point.
2. Active evaluation: Leads add or remove brands from their initial consideration as they actively explore their purchasing options. In contrast to the classic funnel, which shrinks at each stage, the McKinsey model widens during this examination stage to reflect options being weighed.
The risk of losing a lead is combated by anticipating their questions and controlling the dialogue with content. Being prepared with tools to assist the lead’s research can be invaluable in capturing their interest and, eventually, their business.
Providing in-depth and comprehensive information (such as whitepapers and eBooks) is the most effective method to engage leads during the evaluation phase and inform their decision making.
3. Moment of Purchase: This is when leads decide to buy, if the previous stages have proved to be successful. The goal of this step is to make the purchasing experience simple and straightforward. KcKinsey also recommends focusing on improving the user experience (UX) as much as possible at this sales stage.
4. Post-purchase experience: The final phase of the AIDA funnel is all about action. If the strategies in the previous sales funnel stages phases were all effective, including lead nurturing in between, the action phase will result in a purchase. Marketers can further incentivise buyers to take action with content that addresses leads’ final concerns, such as case studies, product demos, and analyst reports.